In order to effectively distribute air throughout a building, the size of ductwork plays a crucial role. The airflow requirements and the distance it needs to travel are the determining factors when it comes to sizing the ductwork. By considering these factors, HVAC professionals can ensure that the airflow is balanced and consistent, resulting in optimal comfort for the occupants. So, whether you’re trying to cool down a large office space or heat multiple rooms in a residential building, understanding the importance of correctly sized ductwork is key.
This image is property of theengineeringmindset.com.
Factors Influencing Ductwork Size
When designing a ductwork system for HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) applications, there are two main factors that influence its size: airflow requirements and the distance the air needs to travel. Properly considering these factors is crucial to ensure efficient and effective airflow throughout the system.
Airflow Requirements
Determining the required airflow is an essential step in sizing ductwork. The amount of air needed to achieve the desired temperature and air quality varies based on factors such as the HVAC system capacity, building occupancy, and ventilation standards.
Determining Airflow
To determine the necessary airflow for a specific application, various considerations come into play. Firstly, the capacity of the HVAC system must be taken into account. This refers to the system’s ability to heat or cool a given space. A larger HVAC system typically requires more significant airflow to distribute the conditioned air effectively.
The building occupancy is another vital factor in determining airflow requirements. Spaces that accommodate a higher number of people, such as offices or assembly halls, require a greater amount of airflow to maintain comfortable conditions and ensure proper ventilation.
Furthermore, ventilation standards established by organizations like ASHRAE (American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers) provide guidelines on the minimum airflow rates necessary to maintain indoor air quality and prevent the buildup of contaminants.
Airflow Calculation
To calculate the required airflow, the industry commonly uses the unit of measurement cubic feet per minute (CFM). CFM represents the volume of air that needs to flow through the ductwork system to achieve the desired comfort level.
The airflow calculation involves performing load calculations, which take into account factors such as the size and insulation of the space, the desired temperature differential, and the heat sources within the area. This helps determine the appropriate CFM needed to adequately heat or cool the space.
ASHRAE guidelines provide a standardized framework for calculating airflow requirements based on factors such as space type, occupancy, and the presence of specific equipment or appliances.
Factors Affecting Airflow
Several factors can impact the airflow within the ductwork system, thereby influencing the required ductwork size. Obstructions and resistance in the airflow path, such as bends, dampers, or filters, can result in pressure drop and reduce the overall airflow capacity. It is essential to consider these factors during the design process to ensure optimal performance.
Another factor to consider is air leakage. Any gaps or leaks in the ductwork can lead to a loss of airflow and result in energy inefficiency. Proper sealing techniques and high-quality ductwork materials can help mitigate air leakage issues.
Additionally, the choice of ductwork material itself can impact airflow. Certain types of duct materials, such as smooth metal ducts, offer less resistance to airflow compared to rougher materials like fiberglass. Selecting the appropriate duct material based on the specific needs of the application is important for maintaining efficient airflow.
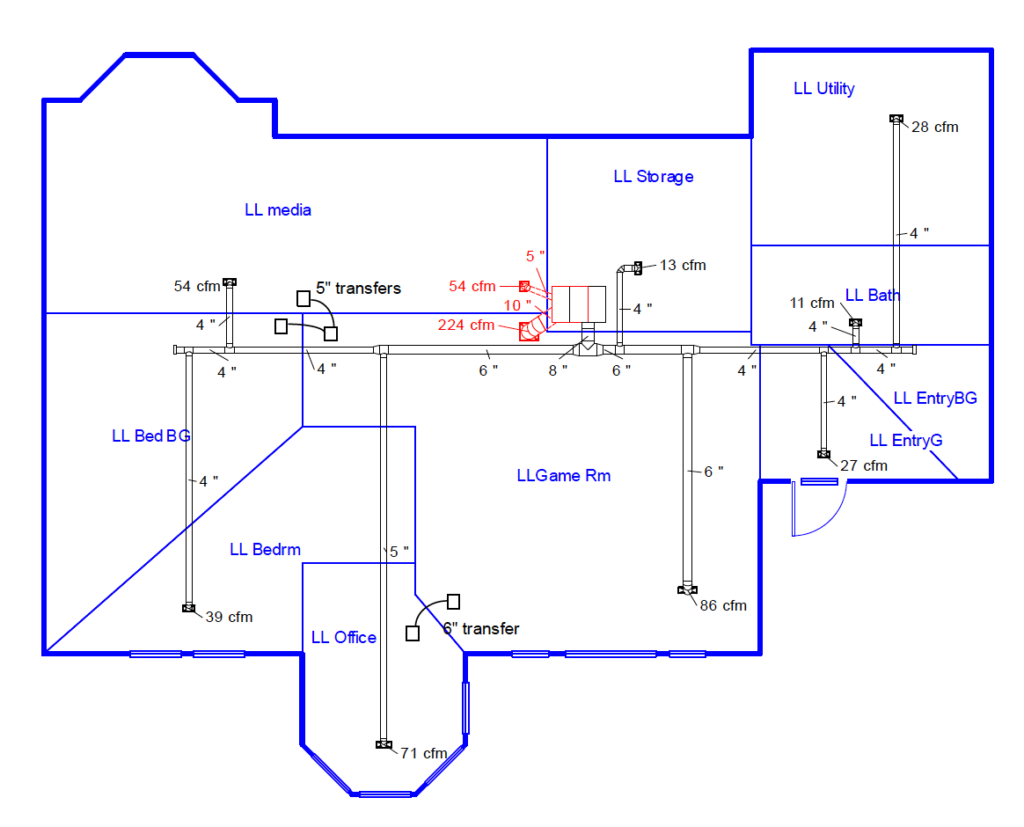
This image is property of i0.wp.com.
Distance of Travel
The distance that the air needs to travel within the ductwork system is another critical factor in determining its size. Factors such as the length of the duct runs, whether they are horizontal or vertical, and the overall layout of the ductwork can impact the system’s performance.
Short vs. Long Duct Runs
The length of the duct runs plays a significant role in the airflow within the system. Longer duct runs introduce additional pressure losses due to friction as the air moves through the ducts. As a result, larger duct sizes may be necessary to compensate for the increased resistance, ensuring that the required airflow is maintained.
On the other hand, shorter duct runs tend to have lower pressure losses and require smaller duct sizes. By keeping the distance between the HVAC system and the delivery points minimal, it becomes easier to maintain the desired airflow rates.
Vertical vs. Horizontal Ductwork
The orientation of the ductwork, whether vertical or horizontal, can also affect the airflow dynamics. In vertical duct runs, the force of gravity can either assist or hinder the airflow, depending on the direction. When airflow goes against gravity, additional pressure may be required to overcome the resistance, potentially necessitating larger duct sizes.
Horizontal ductwork, on the other hand, experiences less influence from gravity. However, it is important to consider any potential variations in static pressure along the horizontal runs and size the ducts accordingly to achieve balanced airflow throughout the system.
Ductwork Layout
The layout of the ductwork system also contributes to its overall efficiency and effectiveness. Straight runs of ductwork provide the most direct path for airflow, minimizing pressure losses. However, bends, transitions, and changes in direction are often inevitable in real-world installations.
Careful consideration must be given to the number and severity of bends, as each introduces additional resistance and pressure drop. By selecting appropriate duct sizes and minimizing the number of bends, air can flow more smoothly and efficiently through the system.
Ductwork Sizing Calculations
To determine the optimal size of ductwork based on the distance of travel, various calculations and methods can be employed. One commonly used technique is the T-Method, which calculates the pressure loss based on the flow rate, duct diameter, and the total equivalent length of the duct system.
The T-Method takes into account the fittings, branches, and other components in the system to provide a more accurate sizing calculation. It helps ensure that the ductwork is sized correctly, considering all the factors that impact airflow and efficiency.
Principle
The T-Method works on the principle of balancing the pressure losses and the airflow resistance throughout the ductwork system. By accounting for the total equivalent length of the duct runs, as well as the specific pressure losses at bends, fittings, and other components, the method helps determine the required duct size to achieve the desired airflow.
Applicability
The T-Method is widely applicable in both residential and commercial HVAC projects. It is particularly useful when dealing with complex ductwork layouts where multiple branches, transitions, and fittings are present. By accurately sizing the ductwork, it helps maintain balanced airflow and prevents excessive pressure losses.
Limitations
While the T-Method is a reliable sizing method, it does have its limitations. It assumes steady-state conditions and does not account for dynamic factors such as airflow variations due to variable speed fans or dampers. Additionally, it relies on accurate input data, including pressure loss coefficients for fittings and components, which must be obtained from reliable sources.
In conclusion, when designing ductwork systems, the size must be carefully determined based on the airflow requirements and the distance the air needs to travel. Factors such as HVAC system capacity, building occupancy, ventilation standards, obstructions, leakage, and ductwork material should be considered to ensure efficient and effective airflow. Additionally, the length, orientation, and layout of the ductwork play a crucial role in determining the appropriate duct size. By considering these factors and utilizing methods like the T-Method, professionals in the HVAC industry can design ductwork systems that optimize performance, maintain comfortable indoor conditions, and enhance energy efficiency.
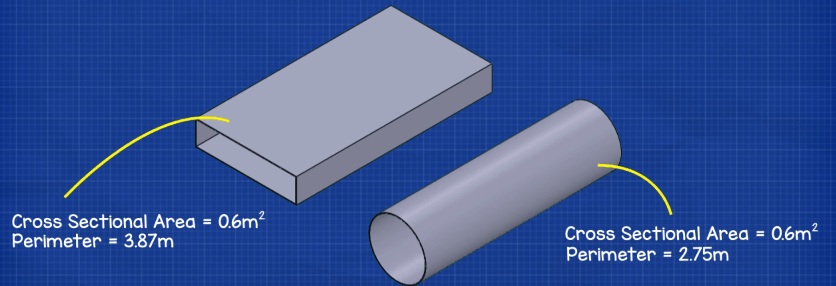
This image is property of theengineeringmindset.com.

