Imagine sitting in a scorching hot room, desperately longing for a cool breeze to provide relief. Luckily, portable air conditioners come to the rescue. Curious minds wonder: how do they work their magic? In this article, we will embark on a journey to unravel the inner workings of these miraculous devices, shedding light on the science behind their cooling capabilities. Whether you’re contemplating investing in one for your home, apartment, or office, understanding the mechanics behind portable air conditioners will surely leave you feeling informed and prepared to beat the heat.
The Basics of Portable Air Conditioners
What is a Portable Air Conditioner?
A portable air conditioner is a compact and self-contained cooling unit that can be easily moved around from one room to another. It operates on the same principles as a central air conditioner, but it is designed for individual cooling in specific spaces. Portable air conditioners are a popular choice for homes, apartments, offices, or any other space where installing a central air conditioning system is not feasible or cost-effective.
How Does a Portable Air Conditioner Differ from a Central Air Conditioner?
While the basic function of both portable air conditioners and central air conditioners is to cool the air, there are a few key differences between the two.
Firstly, portable air conditioners are designed to cool smaller areas, typically ranging from 200 to 500 square feet. In contrast, central air conditioners are capable of cooling an entire home or building.
Secondly, portable air conditioners are standalone units that do not require any permanent installation. They come with venting kits that allow the hot air generated during the cooling process to be vented out through a window or a specially designed hole in the wall. On the other hand, central air conditioners require professional installation as they are connected to an elaborate system of ducts that distribute cooled air throughout the entire building.
Lastly, portable air conditioners offer greater flexibility and mobility as they can be easily moved around to different rooms. Central air conditioners, once installed, are fixed in place and cannot be relocated without substantial effort and expense.
Advantages of Portable Air Conditioners
There are several advantages to using portable air conditioners:
- Cost-effectiveness: Portable air conditioners are generally more affordable than central air conditioning systems. They offer an economical alternative for cooling specific areas of your home or office without the need for a large investment.
- Easy installation: Portable air conditioners are designed for quick and easy installation. They come with all the necessary components and venting kits, allowing you to set up the unit yourself without requiring professional assistance.
- Mobility: One of the key advantages of portable air conditioners is their portability. You can easily move them from room to room, depending on where you need cooling the most. This flexibility allows you to cool specific areas as needed, saving energy and reducing cooling costs.
- No permanent installation required: Unlike central air conditioners, portable units do not require permanent installation. This makes them an ideal cooling solution for renters or people living in apartments where modifying the property is not allowed.
- Versatility: Portable air conditioners are not limited to cooling alone. Many models also offer additional functions such as dehumidification, fan-only mode, and even heating capabilities. This versatility makes them useful all year round, regardless of the weather conditions.
- Energy efficiency: Portable air conditioners are designed to provide efficient cooling while consuming less energy compared to central air conditioners. The ability to cool specific areas rather than an entire building helps in reducing energy waste and lowering utility bills.
Components of a Portable Air Conditioner
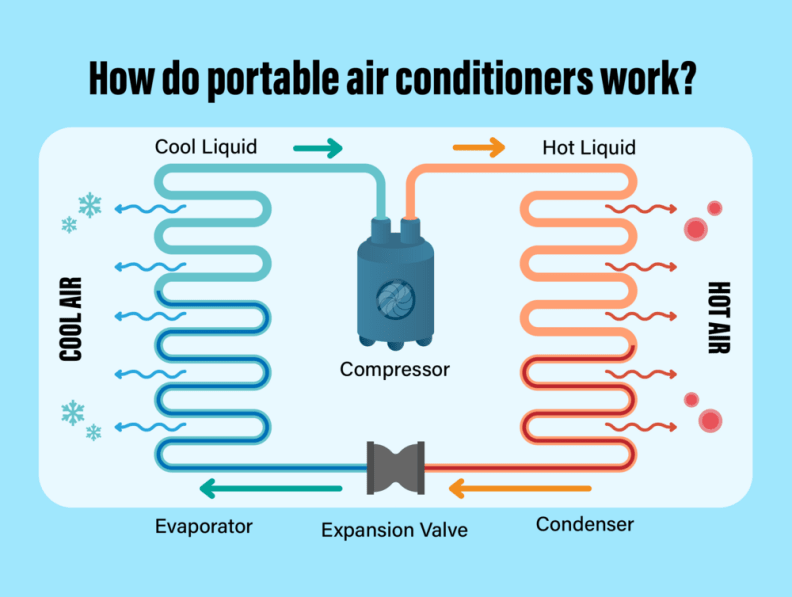
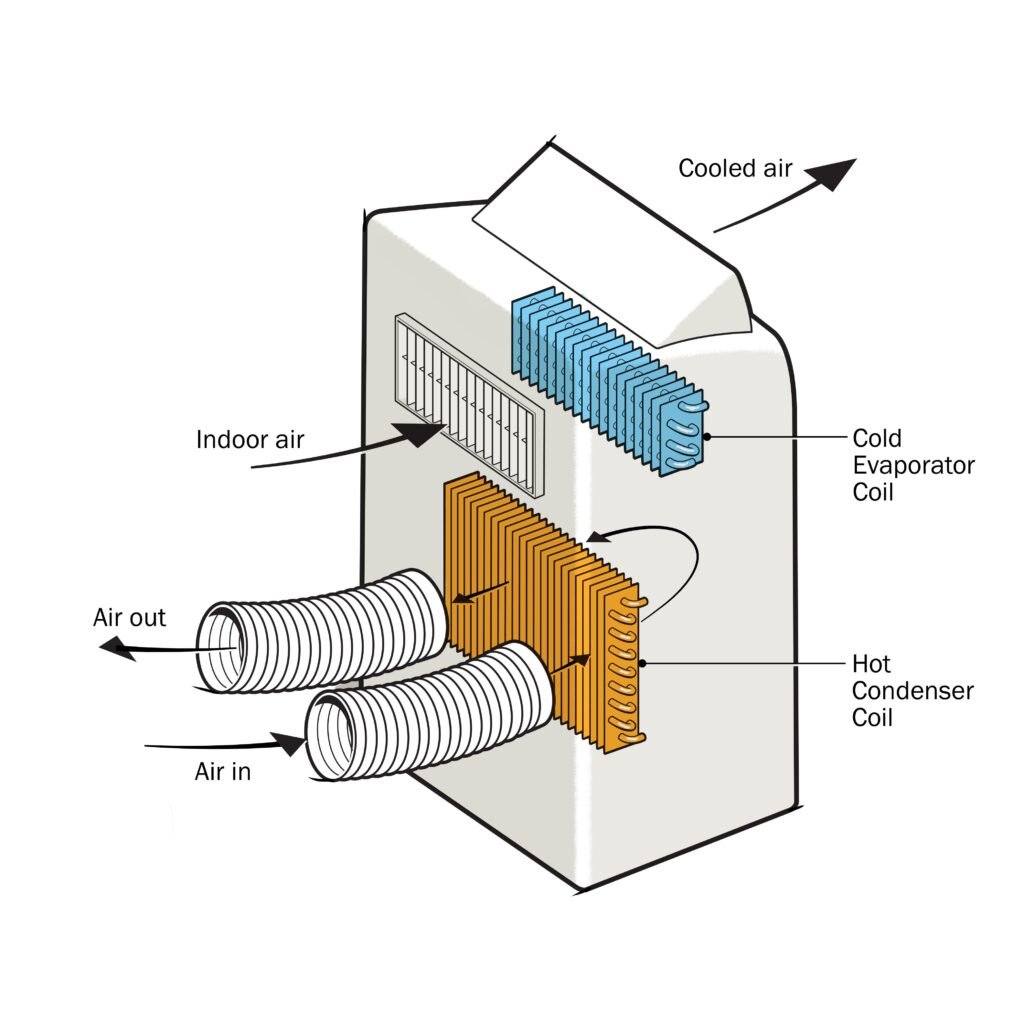
Condenser
The condenser is one of the essential components of a portable air conditioner. It is responsible for releasing heat from the refrigerant. The hot refrigerant gas enters the condenser, where it is cooled down and converted back into a liquid state. The condenser is equipped with metal fins or coils that maximize heat dissipation.
Evaporator
The evaporator is another crucial component of a portable air conditioner. It is directly responsible for cooling the air. The warm indoor air is drawn into the unit and passes over the evaporator coils. The refrigerant inside the evaporator absorbs the heat from the air, resulting in the cooling of the air. The cooled air is then circulated back into the room, while the refrigerant continues on to the compressor.
Compressor
The compressor plays a vital role in increasing the pressure and temperature of the refrigerant gas. It receives low-pressure refrigerant vapor from the evaporator and compresses it into high-pressure vapor. This process raises the temperature of the refrigerant, preparing it for the next stage of the refrigeration cycle.
Expansion Valve
The expansion valve is responsible for regulating the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator. It controls the pressure and flow rate of the refrigerant, allowing it to expand rapidly as it enters the evaporator. This expansion causes the refrigerant to cool down, making it ready to absorb heat from the warm indoor air.
Fan
The fan is an integral part of a portable air conditioner as it helps circulate the air within the unit. There are usually two fans in a portable air conditioner – one for drawing in the warm air from the room and another for expelling the hot air generated during the cooling process. The fan also aids in maintaining a consistent airflow, ensuring efficient cooling and distribution of cooled air.
Exhaust Hose
The exhaust hose serves as the duct through which the hot air generated by the portable air conditioner is expelled to the outside. It extracts the hot air from the condenser and carries it out of the room through a window or a specially designed opening. The exhaust hose should be properly installed and sealed to prevent any hot air from entering back into the room.

This image is property of cdn.shopify.com.
The Refrigeration Cycle
Introduction to the Refrigeration Cycle
The refrigeration cycle is the fundamental principle behind how a portable air conditioner works. It is a continuous cycle in which refrigerant flows through various components, changing its state and absorbing or releasing heat along the way. The refrigeration cycle consists of four primary steps: compression, condensation, expansion, and evaporation.
Step 1: Compression
The refrigeration cycle begins with the compressor. The compressor receives low-pressure, low-temperature refrigerant vapor from the evaporator and compresses it, significantly increasing its pressure and temperature. This compressed refrigerant then moves on to the condenser.
Step 2: Condensation
In the condenser, the hot, compressed refrigerant vapor releases heat to the surrounding environment as it comes into contact with the cooler air or the condenser coils. This heat exchange causes the refrigerant to condense into a high-pressure, high-temperature liquid.
Step 3: Expansion
The high-pressure liquid refrigerant then passes through the expansion valve, which controls the flow and pressure of the refrigerant. As the refrigerant passes through the expansion valve, its pressure drops significantly. This sudden pressure drop causes the refrigerant to cool rapidly, changing it into a low-pressure, low-temperature liquid.
Step 4: Evaporation
The low-pressure, low-temperature liquid refrigerant now enters the evaporator. Here, it absorbs heat from the warm indoor air, causing the refrigerant to evaporate and change back into a low-pressure vapor. The evaporator coils act as a heat exchanger, transferring the heat from the air to the refrigerant. The cooled air is then circulated back into the room, while the refrigerant, now in vapor form, returns to the compressor to begin the cycle again.
Cooling Modes and Temperature Control
Cooling Modes
Portable air conditioners offer various cooling modes to suit different preferences and requirements. The most common cooling modes include:
- Cool Mode: In this mode, the portable air conditioner functions as a standard air conditioner, reducing the temperature of the room to the desired level.
- Fan Mode: In fan mode, the unit operates as a regular fan, circulating the air in the room without actively cooling it. This mode can be useful during cooler days or when you want to create a gentle breeze without lowering the temperature.
- Dehumidifier Mode: Many portable air conditioners have a dehumidifier mode that helps reduce the moisture levels in the air. This mode is especially useful in humid climates or areas prone to dampness.
- Heat Mode (optional): Some portable air conditioners also come with a heat mode, allowing them to function as a heater during colder months. This additional functionality can eliminate the need for separate heating solutions in certain situations.
Temperature Control Options
To provide personalized cooling, portable air conditioners offer temperature control options that allow you to set the desired temperature. The most common options include:
- Manual Control: With manual temperature control, you can adjust the temperature settings using a control panel or a remote control. This allows you to increase or decrease the cooling capacity to achieve the desired comfort level.
- Programmable Timer: Many portable air conditioners come with a programmable timer feature. This allows you to set specific times for the unit to turn on or off automatically. It can be particularly convenient for cooling the room before you arrive home or to conserve energy while you’re away.
- Sleep Mode: Sleep mode is designed to provide a comfortable sleeping environment by gradually adjusting the temperature and fan speed. It helps you achieve a better night’s sleep by maintaining a consistent temperature throughout the night without unnecessary fluctuations.
- Smart Control: Some advanced portable air conditioners are equipped with smart technology, allowing you to control the unit through a smartphone app or voice commands. This feature provides added convenience and flexibility, especially for those who prefer seamless integration with smart home systems.
This image is property of www.appliancesonline.com.au.
Ventilation and Air Circulation
Ventilation Requirements
Proper ventilation is crucial for the effective and efficient operation of a portable air conditioner. It ensures the removal of hot air generated during the cooling process and allows fresh air to circulate in the room. Here are the key ventilation requirements for portable air conditioners:
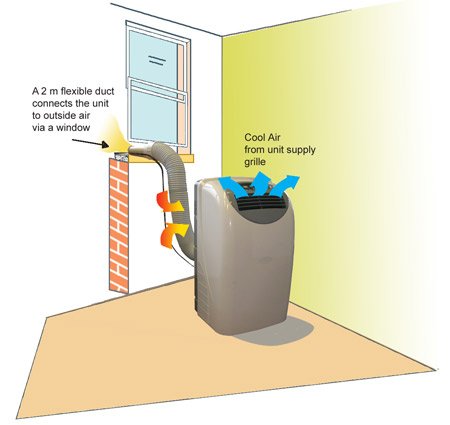
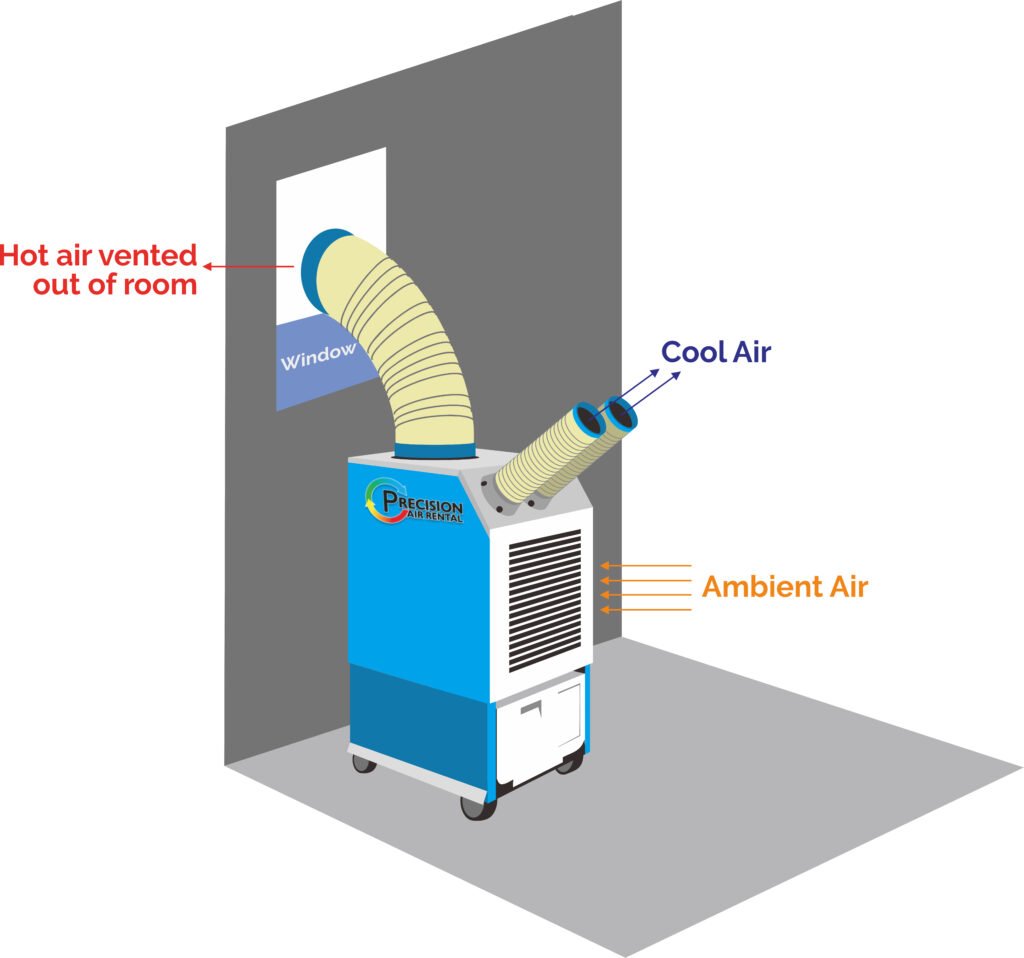
- Window Venting: Most portable air conditioners come with an exhaust hose and a window installation kit. The exhaust hose is connected to the back of the unit and is designed to be routed through a partially opened window. This allows the hot air to be vented outside while preventing the entry of warm air from outside.
- Sliding Door Ventilation: If your space does not have suitable windows, you may consider using a sliding door or a glass panel for ventilation. Special kits are available that allow the exhaust hose to be fitted into the narrow gap between the sliding door and the frame. This ensures efficient ventilation without compromising the security or aesthetics of the space.
- Wall Venting: In certain cases, where window or sliding door ventilation is not feasible, it is possible to vent the portable air conditioner through a specially designed opening in the wall. This requires professional installation to ensure proper sealing and structural integrity.
It is important to note that portable air conditioners should not be vented into attics, crawl spaces, or enclosed areas without proper ventilation. This can result in the recirculation of hot air back into the room, reducing the cooling efficiency of the unit.
Air Circulation
In addition to ventilation, proper air circulation within the room is essential for achieving optimal cooling. Here are a few tips to ensure effective air circulation:
- Clear Obstructions: Ensure that there are no objects blocking the airflow around the portable air conditioner. Keep furniture, curtains, or any other items away from the unit, allowing unrestricted airflow.
- Positioning of the Unit: Place the portable air conditioner in a central location within the room so that it can distribute the cooled air evenly. Avoid placing it near walls or corners that can obstruct the air circulation.
- Use of Fans: To enhance air circulation, you can use additional fans in conjunction with the portable air conditioner. Place oscillating fans strategically to help in spreading the cooled air across the room.
- Open Interior Doors: Keep interior doors open to promote better airflow throughout the space. This ensures that cool air reaches all areas of the room, providing consistent cooling.
Installation and Set-Up
Choosing the Right Location
Selecting the proper location for your portable air conditioner is crucial to ensure efficient cooling. Here are a few factors to consider when choosing the placement:
- Proximity to a Window: As portable air conditioners require window venting, it is essential to position the unit near a suitable window. This ensures a shorter and more efficient exhaust hose installation.
- Level Surface: Place the portable air conditioner on a level surface to prevent any shaking or vibrations during operation. Uneven surfaces can affect the performance of the unit and contribute to excessive noise.
- Access to Power Outlet: Ensure that the chosen location is within reach of a power outlet to connect the unit without the need for extension cords. Using extension cords can lead to power inefficiencies and potential safety hazards.
- Space Constraints: Consider the available space in the room and choose a location that allows easy movement around the unit. Allowing sufficient space for air circulation and maintenance is essential.
Exhaust Hose Installation
Correct installation of the exhaust hose is crucial for the proper operation of a portable air conditioner. Follow these steps for a successful installation:
- Connect the Hose: Attach one end of the exhaust hose to the designated outlet on the back of the portable air conditioner. Ensure a secure connection by twisting the hose clockwise until it is firmly in place.
- Window Installation Kit: Most portable air conditioners come with a window installation kit that includes a window panel and a sliding connector. Insert the window panel into the open window or the gap between the sliding door and the frame, depending on the chosen ventilation method. Adjust the panel to fit tightly and securely.
- Install the Hose: Connect the other end of the exhaust hose to the sliding connector on the window panel. Secure it in place by tightening the hose clamp provided with the unit. Ensure that the connection is airtight to prevent any hot air from entering the room.
- Sealing the Gap: To ensure proper insulation and prevent hot air infiltration, use weatherstripping or insulation tape to seal any gaps around the window panel or sliding connector.
These steps may vary depending on the specific model of the portable air conditioner, so it is essential to refer to the manufacturer’s instructions for detailed guidance.
Electrical Connections
Before connecting your portable air conditioner to a power outlet, be sure to consider these electrical guidelines:
- Power Requirements: Check the power requirements of the portable air conditioner to ensure that it matches the available power supply. Using a power outlet with a lower rating may lead to the unit not functioning optimally or even causing electrical issues.
- Dedicated Circuit: Whenever possible, connect the portable air conditioner to a dedicated circuit to reduce the risk of overloading the electrical system. Sharing a circuit with other high-power appliances can lead to tripped breakers or blown fuses.
- GFCI Outlet: If the portable air conditioner is intended for use in a bathroom or any area with high moisture content, ensure that the power outlet is a Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) outlet. GFCI outlets provide added protection by cutting off power in case of electrical faults.
- Extension Cords: Avoid using extension cords to connect the portable air conditioner. It is best to plug the unit directly into a power outlet to ensure uninterrupted power supply and safe operation.
Always adhere to electrical safety guidelines and consult a professional electrician if you have any doubts or specific requirements.
This image is property of reviewed-com-res.cloudinary.com.
Maintenance and Care
Cleaning and Filter Replacement
Regular cleaning and filter replacement are critical for maintaining the optimal performance and efficiency of your portable air conditioner. Follow these steps:
- Unplug the Unit: Before cleaning, make sure the portable air conditioner is completely turned off and unplugged from the power outlet.
- Clean the Exterior: Wipe the exterior surfaces of the unit with a damp cloth to remove any dust or debris. Avoid using harsh chemicals or abrasive cleaners that may damage the finish.
- Filter Cleaning or Replacement: Portable air conditioners are equipped with filters that trap dust, allergens, and other particles from the air. Refer to the manufacturer’s instructions for guidance on cleaning or replacing the filters. Some units have washable filters that can be rinsed with water and air-dried, while others require replacement filters.
- Coil Cleaning: Over time, the evaporator and condenser coils may accumulate dust and dirt, reducing the cooling efficiency. Using a soft brush or a vacuum cleaner with a brush attachment, carefully clean the coils to remove any debris. Take care not to bend or damage the delicate fins.
- Drain Pan Cleaning: If your portable air conditioner has a built-in condensate drain pan, inspect it regularly for any standing water or debris. Clean the drain pan as per the manufacturer’s instructions to prevent clogs or the growth of mold and mildew.
Regular cleaning and filter replacement should be carried out at least once every few weeks or as recommended by the manufacturer. This ensures that your portable air conditioner operates efficiently and provides clean, healthy air.
Condensate Removal
Portable air conditioners produce condensate as a byproduct of the cooling process. Depending on the model, the condensate is either collected in a condensate tank or is automatically evaporated and expelled along with the hot air through the exhaust hose. Here are the steps to handle the condensate:
- Condensate Tank: If your portable air conditioner has a condensate tank, it is important to empty it regularly to prevent overflow. Consult the manufacturer’s instructions for the location of the tank and the recommended frequency of emptying. A full tank can trigger an automatic shut-off or result in water leakage if not addressed promptly.
- Continuous Drainage Option: Some portable air conditioners offer a continuous drainage option, allowing the condensate to be drained directly through a hose. If this option is available, connect a drain hose to the designated outlet and ensure it is properly routed to a suitable drainage point. Regularly check for any blockages in the hose to maintain efficient drainage.
It is crucial to address condensate removal to prevent water damage, maintain optimal performance, and ensure a comfortable indoor environment.
Regular Inspections
In addition to regular cleaning and maintenance, periodic inspections are essential to detect any potential issues or abnormalities. Here are aspects to focus on during inspections:
- Hose and Vent: Inspect the exhaust hose and window panel for any leaks, cracks, or loose connections. Ensure that the windows or sliding doors are properly sealed to prevent hot air from entering the room.
- Fan and Blower: Check the fan blades and blower for any signs of dirt, dust, or debris buildup. Clean them carefully to ensure optimal airflow and prevent any potential obstructions.
- Electrical Connections: Inspect the power cord and plug for any damage or fraying. If you notice any issues, contact a professional technician to handle any necessary repairs.
- Airflow and Cooling Efficiency: Periodically test the cooling performance of your portable air conditioner. Monitor the airflow and temperature to ensure that the unit is providing the desired cooling effect. If there are any substantial changes in cooling efficiency, consult the manufacturer or a professional technician for troubleshooting.
By conducting regular inspections, you can address any minor issues before they escalate and ensure that your portable air conditioner continues to operate effectively.
Energy Efficiency and Noise Levels
Energy Efficiency Ratings
Energy efficiency is an important consideration when choosing a portable air conditioner. Look for the following factors to determine the energy efficiency of a unit:
- Energy Efficiency Ratio (EER): The EER is a measure of the cooling capacity of the air conditioner per unit of electrical energy consumed. Higher EER ratings indicate greater energy efficiency. Look for units with higher EER ratings to save on energy costs.
- ENERGY STAR Certification: ENERGY STAR certified portable air conditioners meet strict energy efficiency guidelines set by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. These units are designed to provide superior energy efficiency and can help reduce your carbon footprint while saving on electricity bills.
- Programmable Features: Portable air conditioners with programmable timers and temperature control options allow you to set specific operating schedules and desired temperatures. This feature helps optimize energy usage by cooling the room only when necessary.
Considering these energy-efficient features can help you select a portable air conditioner that meets your cooling requirements while keeping energy consumption to a minimum.
Noise Levels
Noise levels can significantly impact the comfort of your living or working space. Portable air conditioners generate noise during operation, primarily from the compressors and fans. Here are a few factors to consider regarding noise levels:
- Decibel (dB) Rating: The decibel rating indicates the sound level emitted by the portable air conditioner. Lower dB ratings mean quieter operation. Look for units with lower dB ratings if noise is a concern.
- Two-Speed or Variable-Speed Fans: Portable air conditioners with adjustable fan speeds offer more control over noise levels. Lower fan speeds produce less noise while providing sufficient cooling for smaller areas.
- Sleep Mode: Some portable air conditioners have a sleep mode feature that gradually reduces the fan speed and noise level during nighttime operation. This allows for a quiet sleeping environment without compromising cooling comfort.
- Placement and Insulation: Proper unit placement and installing insulation around the exhaust hose and window panel can reduce noise transmission. Placing the unit on a vibration-damping mat or using sound-absorbing materials can also help minimize noise.
By considering these aspects, you can select a portable air conditioner that provides efficient cooling while maintaining a peaceful and quiet environment.
This image is property of hips.hearstapps.com.
Common Portable Air Conditioner Issues
Insufficient Cooling
If your portable air conditioner is not providing sufficient cooling, there could be several potential causes:
- Undersized Unit: Ensure that the cooling capacity of your portable air conditioner matches the size of the room or area you intend to cool. If the unit is too small for the space, it may struggle to cool effectively.
- Inadequate Ventilation: Check the exhaust hose for any obstructions or improper installation. Proper ventilation is crucial for efficient cooling, as it allows the hot air to be expelled outside while bringing in fresh air.
- Dirty Filters or Coils: Dirty filters or coils can restrict airflow, reducing the cooling efficiency of the unit. Clean or replace the filters as recommended by the manufacturer. Additionally, periodically clean the coils to remove any dust or debris buildup.
- Overheating: Portable air conditioners can overheat if they are operating continuously without proper rest or if the ambient temperature is too high. Allow the unit to cool down for a while and consider reducing the cooling load or increasing ventilation.
If the issue persists, it is advisable to consult the manufacturer’s troubleshooting guide or contact a professional technician for assistance.
Water Leakage
Water leakage from a portable air conditioner can be a result of the following factors:
- Full Condensate Tank: If your portable air conditioner has a condensate tank, it may overflow if not emptied regularly. Check the tank and empty it as recommended by the manufacturer to prevent water leakage.
- Improper Drainage: If your portable air conditioner has a continuous drainage option, ensure that the drain hose is properly connected and not clogged. Check for any blockages in the drain hose or the drainage route.
- Condensate Pump Failure: Some portable air conditioners feature a condensate pump for automatic water removal. If the pump malfunctions or becomes clogged, it may result in water leakage. Refer to the manufacturer’s instructions to troubleshoot or seek professional assistance.
- Improper Installation: Water leakage can occur if the portable air conditioner is not properly installed or if the window kit and exhaust hose are not sealed tightly. Check for any gaps or loose connections, and ensure that the unit is installed as per the manufacturer’s instructions.
Consulting with the manufacturer or a professional technician can help identify the specific cause of the water leakage and facilitate a proper solution.
Excessive Noise
While portable air conditioners inherently produce some level of noise during operation, excessive noise can be a cause for concern. Here are some possible causes and solutions:
- Loose Components: Vibrating or loose components within the unit can create unnecessary noise. Check all screws, panels, and fasteners to ensure they are tight and secure. Tightening or adjusting these components may help reduce noise levels.
- Fan or Blower Issues: Dirt, dust, or debris accumulation on the fan blades or blower can cause noise. Carefully clean the fan and blower to remove any obstructions and restore smooth operation.
- Refrigerant Leaks: Refrigerant leaks can lead to hissing or hissing noises. If you suspect a refrigerant leak, it is best to contact a professional technician to identify and repair the issue.
- Unit Placement: Improper placement of the portable air conditioner can contribute to excessive noise. Make sure the unit is on a level surface and away from any objects that may obstruct airflow or contribute to vibrations.
If the noise persists and is disruptive, it is recommended to consult the manufacturer or seek professional assistance for further inspection and resolution.
Electrical Problems
Electrical problems in portable air conditioners can manifest in different ways, including power interruptions, tripped breakers, or failure to turn on. Here are a few troubleshooting steps to consider:
- Power Supply: Check if the power outlet is functioning properly by plugging in another device. If the outlet is not supplying power, reset the breaker or replace any blown fuses as necessary.
- Power Cord: Inspect the power cord for any visible damage, fraying, or loose connections. If there are any issues, contact a professional electrician or the manufacturer for proper repair or replacement.
- Faulty Controls: If the unit does not respond to any control inputs, it may indicate a fault in the control panel or circuit board. Contact the manufacturer or a professional technician for further diagnosis and repair.
Remember that electrical issues can be dangerous to handle without proper knowledge or experience. If you are uncertain or unable to troubleshoot the problem, it is advisable to seek professional assistance.
Usage Tips and Best Practices
Sizing Considerations
When selecting a portable air conditioner, it is important to choose the right size for your space. Factors to consider include the room size, insulation, ceiling height, and heat-generating sources. Undersized units may struggle to cool effectively, while oversized units may cycle on and off frequently, leading to inefficient operation. Refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines or consult with a professional to determine the appropriate cooling capacity for your specific needs.
Proper Use of Ventilation Kits
Proper installation and use of the included window installation kit and exhaust hose are vital for efficient cooling. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully to ensure a tight seal and smooth airflow. Regularly inspect the installation components and recheck the connections to prevent any air leakage or entry of unwanted warm air.
Setting the Optimal Temperature
Setting the optimal temperature is crucial to ensure efficient cooling while avoiding unnecessary energy consumption. Aim for a comfortable temperature rather than a very low setting. A temperature range between 72 to 78 degrees Fahrenheit is generally recommended for a balanced balance between cooling comfort and energy efficiency.
Maximizing Efficiency
To maximize the efficiency of your portable air conditioner, consider these tips:
- Close Doors and Windows: Keep doors and windows closed when the portable air conditioner is in operation to prevent any unwanted heat sources from entering the room.
- Use Curtains or Blinds: Utilize curtains or blinds to block out direct sunlight, reducing the heat load on the portable air conditioner and minimizing cooling requirements.
- Seal Leaks and Insulate: Inspect the room for any air leaks around windows, doors, or other openings. Seal any gaps or cracks with weatherstripping or other insulation materials to minimize air infiltration.
- Reduce Heat Sources: Minimize the use of heat-generating appliances or lighting during hot periods. These sources can increase the cooling load and reduce the overall efficiency of the portable air conditioner.
By implementing these practices, you can optimize the cooling performance of your portable air conditioner and reduce energy consumption.
In conclusion, portable air conditioners provide a practical and versatile cooling solution for homes, apartments, and offices. Understanding their components, the refrigeration cycle, cooling modes, ventilation requirements, and maintenance needs can help you make informed decisions and ensure optimal performance. By following proper installation and usage guidelines, you can create a comfortable and cool environment while maximizing energy efficiency and minimizing common issues. Stay cool and enjoy the benefits of a portable air conditioner throughout the year.
This image is property of precisionairrental.com.au.